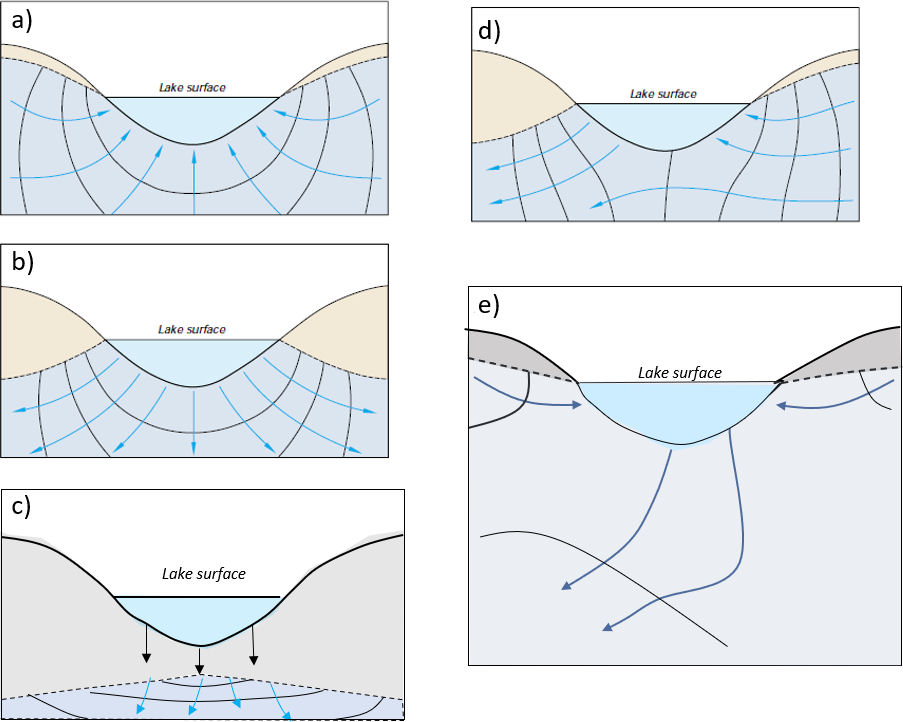
3 Lakes and Groundwater Exchange
Groundwater exchange with lakes can be conceptualized using the cross sections presented in Figures 4 through 8. The surface water represented in these generic conceptual models can be viewed as representing ponds and lakes at various scales. Following Winter and others (1998), lake-groundwater exchange is shown using five, cross-sectional conceptual models (Figure 32a-e). A mixed-exchange condition has been added to the lake conceptual model and the zero-exchange scenario has been omitted as it is not likely to occur or be identified in most settings. Early conceptual models of lakes assumed they were isolated from the groundwater systems by low conductivity bottom sediments. As groundwater-lake research expanded, the systems were recognized as interconnected (e.g., Born et al., 1974).
Lakes also tend to trap sediments from runoff, streamflow and or shoreline erosion. These deposits typically cover all or portions of the lake bottom and are usually organic-rich, finer-grained and of lower hydraulic conductivity than the materials in which the lake formed. The presence of low hydraulic conductivity sediments can limit the rates and locations of exchange. For the conceptual models of lake and groundwater exchange presented here, it is assumed that exchange is a function of the location of the lake in the adjacent groundwater system and that bottom sediment characteristics do not control overall groundwater exchange conditions. A discussion of more complex exchange settings follows the initial development of exchange models.