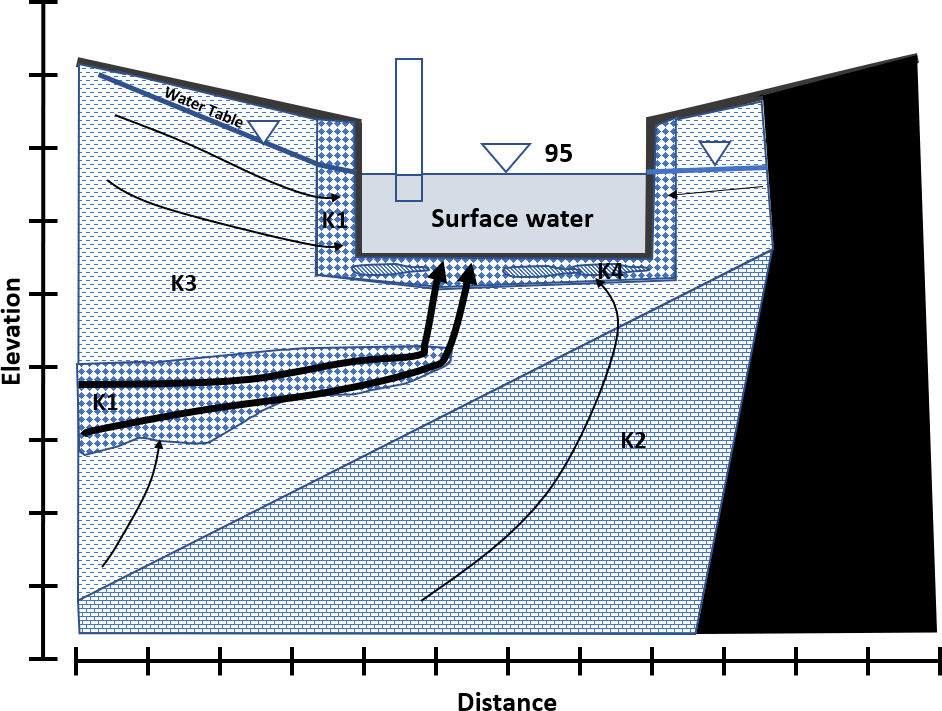
1.7 Heterogeneity in Exchange
The conceptual models of groundwater-surface water exchange presented in previous sections are uncomplicated as they illustrate exchanges under isotropic and homogeneous hydrogeological conditions. Location and magnitude of exchange to and from surface-water features are dependent on the natural distribution of heads, hydraulic conductivity, anisotropy distributions, and boundary conditions (Figure 10). The presence of anisotropic conditions, within the constraints of the head distribution, will direct flow preferentially to zones of higher hydraulic conductivity. In general, earth materials with low permeabilities will limit the movement of exchange waters in the subsurface. When evaluating exchange conditions at some sites, an increased level of detail is required to capture locations and magnitudes of exchange as the study area becomes smaller.